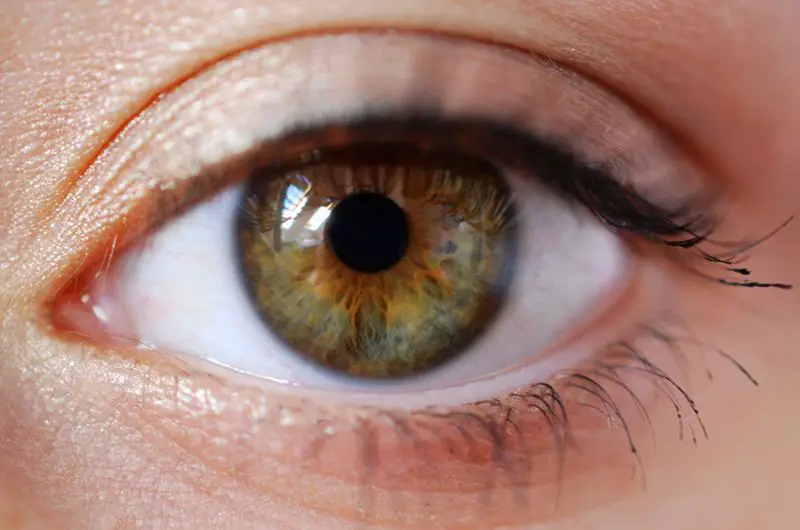
Hazel is a light brownish color that is often used to describe eyes. The exact shade can vary quite a bit from person to person. Here’s a closer look at the color hazel, what it means, and how it relates to eyes.
The Meaning of Hazel
The word “hazel” traces back to Old English “hæsel” referring to the hazelnut tree. The name transferred to the light brown color of the hazelnut shell.
So hazel as a color refers to the brownish-greenish shade of hazelnut shells. It’s a pale brown with a slight greenish, yellowish, or grayish tinge.
Some specific shades that fall under the “hazel” umbrella are:
– Light brown
– Tan
– Taupe
– Grayish brown
– Yellowish brown
– Greenish brown
The color arises from a mix of light brown and varying amounts of other hues like green, yellow, and gray. This results in the subtle variation seen among hazel eyes.
How Hazel Relates to Eyes
Hazel is commonly used as a descriptor for eye color. Hazel eyes appear light brown or tan, sometimes with flecks or ripples of green, gold, or reddish brown.
Here are some key things to know about hazel eyes:
– They have a mix of melanin pigments. Hazel eyes contain a combination of melanin colors. Mostly they contain brown eumelanin. But they can also contain some yellow and black pigments.
– They can look different shades. Hazel eye color can shift looking more green, brown, or gold depending on lighting conditions. The distribution of melanin isn’t always even, creating different patterns and concentrations of color across the iris.
– They are genetically complex. Hazel eye color is not defined by a single gene like blue or brown eyes. Multiple genes influence the different melanin pigments in hazel irises, which is why the shade can vary so much.
– They are fairly uncommon. Only about 5-10% of people worldwide have hazel eyes. Brown eyes are the most common, while hazel eyes are much rarer.
The Spectrum of Hazel Eye Colors
Hazel eyes come in many shades, ranging from light brown to nearly amber or golden. Here’s a look at some of the most common hazel eye color variations:
Brownish-Hazel
Many hazel eyes appear primarily light brown in color, with just the faintest hints of other hues mixed in. This results in a brownish-hazel eye color.
Greenish-Hazel
When hazel eyes contain noticeable flecks or ripples of green, the overall effect is a greenish-hazel color. The green may be more concentrated around the pupil or distributed across the iris.
Golden-Hazel
Some hazel eyes verge on amber or gold hue. This golden-hazel eye color comes from a higher concentration of yellow melanin pigment.
| Hazel Eye Color | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Brownish-hazel | Mostly light brown with faint hints of other colors mixed in |
| Greenish-hazel | Light brown with visible green flecks or ripples |
| Golden-hazel | Light brown mixed with a rich amber/gold color |
This table summarizes the most common hazel eye color variations. The diversity comes down to differences in the concentration and distribution of melanin pigments.
How Lighting Affects Hazel Eyes
The way hazel eyes look can shift subtly depending on the lighting conditions:
– Natural daylight brings out the hints of green, gold, and other colors mixed into the light brown base. You see the most color variations in hazel eyes outdoors on a sunny day.
– Under warm incandescent lighting, hazel eyes may look more golden-brown. The yellow tones are emphasized.
– In fluorescent lighting, hazel eyes might appear paler and cooler-toned. The light brown color becomes more muted.
– Dim conditions can make hazel eyes look darker brown, as the pupil dilates and other flecks of color are obscured.
So hazel eyes are chameleonic. While the genetics remain the same, the balance of different melanin pigments causes the color to come across somewhat differently in various lighting scenarios.
Hazel Eyes in Infants & Children
Hazel eyes are very rare in infants. Almost all babies are born with blue or grayish-blue eyes. Melanin pigmentation continues to develop as the child grows.
Here is the typical eye color progression:
– 6-12 months: True eye color starts to become apparent as melanin increases. Hazel eyes emerge as light brown.
– 1-2 years old: More melanin develops, revealing hints of green, gold, or other colors mixed with light brown.
– 3-5 years old: Eye color is established but may continue to get subtly darker into early childhood.
Eye color can still shift slightly in hazel eyes through childhood. But by age 5-7, the hazel color is fully developed and stabilized barring any major health changes.
Hazel Eyes Around the World
Hazel eyes appear in people across all different ethnicities and races worldwide. However, they are more commonly seen in certain populations:
– Northern, Eastern, and Western Europeans are the most likely to have hazel eyes. Estimates range from 5-20% across different European countries.
– Hazel eyes are less common in Southern Europeans, under 5% in countries like Spain, Italy, and Greece.
– In North Africa and the Middle East, hazel eyes are very rare, under 1% prevalence.
– Hazel eyes occur in 2-5% of the population across most of Asia and the Americas in non-European individuals.
– There are almost no naturally occurring hazel eyes among indigenous Aboriginal Australians or sub-Saharan Africans.
So while possible in diverse populations, hazel eyes are most likely to appear in those of European descent due to selective pressure over human evolution.
How Hazel Eyes Get Their Color
The range of possible hazel eye colors stems from the specific mix of melanin pigments:
– **Eumelanin** – Brown and black melanin, creates the predominant brown hue in hazel eyes.
– **Pheomelanin** – Red and yellow melanin, adds golden/amber tones.
– **Neuromelanin** – Gray melanin, contributes slate gray shades.
Levels of these melanins are influenced by over a dozen different genes identified thus far. The OCA2 and HERC2 genes play major roles in determining hazel eye color.
Having one or two copies of the dominant HERC2 variant reduces overall eumelanin production in the iris, causing hazel eyes rather than dark brown. At the same time, pheomelanin and neuromelanin levels vary, resulting in the range of possible hazel shades.
Comparing Hazel to Other Eye Colors
How do hazel eyes stack up against other possible iris shades? Here’s a quick rundown:
– **Brown eyes** – Most concentrated melanin content
– **Hazel eyes** – Moderate melanin concentration
– **Amber eyes** – Similar color to hazel but brighter and more golden
– **Green eyes** – Low melanin content with some pheomelanin
– **Gray eyes** – Very low melanin levels with more neuromelanin
– **Blue eyes** – Minimal melanin, some collagen scattering of light
Hazel eyes fall somewhere in the middle of the eye color spectrum in terms of melanin concentration. Brown has more, while green, gray, blue, and amber have less.
Fun Facts About Hazel Eyes
Beyond the genetics and pigmentation, here are some fun trivia tidbits about hazel peepers:
– Hazel eyes are found more frequently in women than men.
– People with hazel eyes are thought to be more empathetic, sensitive, and emotional compared to those with lighter eye colors.
– Hazel-eyed individuals may have some advantages in low-light vision compared to those with lighter irises.
– Some contacts brands like FreshLook offer colored lenses in hazel shades to mimic natural eye colors.
– Hazel eyes are celebrated in songs like “Hazel Eyes” by the Dave Matthews Band and referenced in books such as The Fault in Our Stars by John Green.
– Famous celebrities with hazel eyes include Harry Styles, Marilyn Monroe, and Shawn Mendes.
So in summary, hazel eyes have mystique and are one of the rarest eye colors. Their unique mix of melanin offers an eye color that is versatile, complex, and shifting like no other.
Conclusion
Hazel is a light brownish color with hints of gold, green, or gray mixed in. When used to describe eyes, it refers to an iris containing various melanin pigments that make the color appear multi-faceted or changeable. Hazel eye color ranges from brownish-green to golden depending on melanin concentration and lighting. While possible in all ethnicities, hazel eyes are rarest among those of African, Asian, and Southern European descent, and most common in Northern Europeans. Their beauty comes from the delicate balance of melanins that come together to produce a distinctive, dimensional eye color.